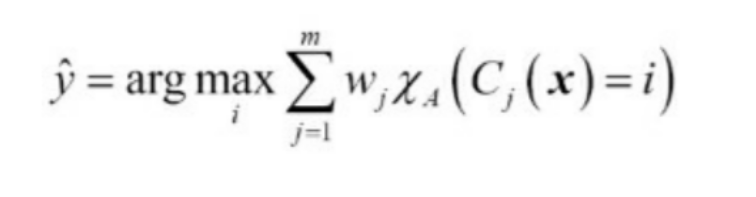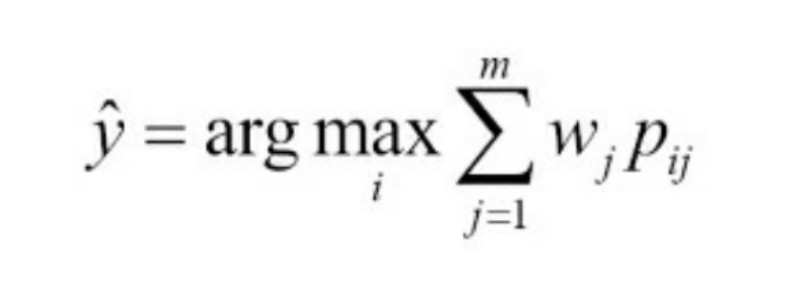과반수 투표(Majority voting) & 다수결 투표(Plurality voting)
과반수 투표와 다수결 투표를 구분하여 사용하고 있다.
하지만 사실 다수결 투표를 이진 분류에 적용하면, 자동으로 과반수 투표가 된다.
따라서 일반적으로 다수결이 널리 통용되는 용어이다.
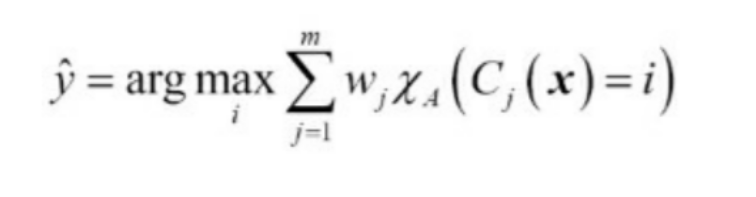
가중치가 적용된 다수결 투표
w는 개별 분류기 C에 연관된 가중치 y는 앙상블이 예측한 클래스의 레이블, A는 고유한 클래스 레이블의 집합
카이(chi)는 특성 함수 또는 지시함수를 말한다.
w 동일 할 경우
mode(C)로 분류기가 예측한 모델의 최빈값을 예측한다.
w가 [0.2, 0.2, 0.6], C(x)가 [0, 0, 1] 일때 예측값
import numpy as np
np.argmax(np.bincount([0, 0, 1], weights=[0.2, 0.2, 0.6]))
로지스틱 회귀에서 클래스 레이블 대신 클래스 레이블의 확률을 반환 했던 것처럼
다수결 투표에서도 예측 클래스 확률을 사용하는 것이 좋다.
클래스 레이블0을 예측할 확률이 각각 0.9, 0.8, 0.4이고 가중치가 [0.2, 0.2, 0.8]일 때의 예측값
ex=np.array([[0.9, 0.1],[0.8, 0.2], [0.4, 0.6]])
p=np.average(ex, axis=0, weights=[0.2, 0.2, 0.6])
p
np.argmax(p)
from sklearn.base import BaseEstimator
from sklearn.base import ClassifierMixin
from skelearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.base import clone
from sklearn.pipeline import _name_estimators
import numpy as np
import operator
import six
class MajorityVoteClassifier(BaseEstimator, ClassifierMixin):
def __init__(self, classifiers, vote='classlabel', weights=None):
self.classifiers=classifiers
self.named_classifiers={key:value for key, value in _name_estimators(classifiers)}
self.vote=vote
self.weights=weights
def fit(self,X,y):
if self.vote not in('probability', 'classlabel'):
raise ValueError("vote는 'probability'또는 'classlabel'이어야 합니다.; (vote=%r)이 입력되었습니다." %self.vote)
if self.weights and len(self.weights)!=len(self.classifiers):
raise ValueError('분류기와 가중치 개수는 같아야 합니다.; 가중치 %d개, 분류기 %d개' %(len(self.weights), len(self.classifiers)))
self.lablenc_=LabelEncoder()
self.lablenc_.fit(y)
self.classes_=self.lablenc_.classes_
self.classifiers_=[]
for clf in self.classifiers:
fitted_clf=clone(clf).fit(X, self.lablenc_.transform(y))
self.classifiers_.append(fitted_clf)
return self
def predict(self, X):
if self.vote=='probability':
maj_vote=np.argmax(self.predict_proba(X), axis=1)
else:
predictions=np.asarray([clf.predict(X) for clf in self.classifiers_]).T
maj_vote=np.apply_along_axis(lambda x: np.argmax(np.bincount(x, weights=self.weights)), axis=1, arr=predictions)
maj_vote=self.lablenc_.inverse_transform(maj_vote)
return maj_vote
def predict_proba(self, X):
probas=np.asarray([clf.predict_proba(X) for clf in self.classifiers_])
avg_proba=np.average(probas, axis=0, weights=self.weights)
return avg_proba
def get_params(self, deep=True):
if not deep:
return super(MajorityVoteClassifier, self).get_params(deep=False)
else:
out=self.named_classifiers.copy()
for name, step in six.iteritems(self.named_classifiers):
for key, value in six.iteritems(step.get_params(deep=True)):
out['%s__%s' %(name, key)]=value
return out
_name_estimators 함수를 이용해서 각 분류기의 매개변수에 접근
위의 VotingClassifier(MajorityVoteClassifier 클래스)는 sklearn.ensemble.VotingClassifier로 사용할 수 있다.
다수결 투표 방식을 사용한 예측(붓꽃 데이터셋)
from sklearn import datasets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
iris=datasets.load_iris()
X, y=iris.data[50:, [1, 2]], iris.target[50:]
le=LabelEncoder()
y=le.fit_transform(y)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test=\
train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.5, random_state=1, stratify=y)
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
import numpy as np
clf1=LogisticRegression(penalty='l2', C=0.001, random_state=1)
clf2=DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=1, criterion='entropy', random_state=0)
clf3=KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1, p=2, metric='minkowski')
pipe1=Pipeline([['sc', StandardScaler()], ['clf', clf1]])
pipe3=Pipeline([['sc', StandardScaler()], ['clf', clf3]])
clf_labels=['Logistic regression', 'Decision tree', 'KNN']
print('10-겹 교차 검증:\n')
for clf, label in zip([pipe1, clf2, pipe3], clf_labels):
scores=cross_val_score(estimator=clf, X=X_train, y=y_train, cv=10, scoring='roc_auc')
print('ROC AUC: %0.2f (+/- %0.2f) [%s]' %(scores.mean(), scores.std(), label))
ROC AUC: 0.92 (+/- 0.15) [Logistic regression]
ROC AUC: 0.87 (+/- 0.18) [Decision tree]
ROC AUC: 0.85 (+/- 0.13) [KNN]
로지스틱 회귀와 k-최근점 이웃 분류기는 결정 트리와는 달리 스케일에 민감하다.
붓꽃 데이터셋의 특성이 모두 같은 cm 단위로 측정되었지만, 특성을 표준화 전처리 하는 것이 좋다.
Majority voting
mv_clf=MajorityVoteClassifier(classifiers=[pipe1, clf2, pipe3])
clf_labels+=['Majority voting']
all_clf=[pipe1, clf2, pipe3, mv_clf]
for clf, label in zip(all_clf, clf_labels):
scores=cross_val_score(estimator=clf, X=X_train, y=y_train, cv=10, scoring='roc_auc')
print('ROC AUC: %0.2f (+/- %0.2f) [%s]' %(scores.mean(), scores.std(), label))
ROC AUC: 0.92 (+/- 0.15) [Logistic regression]
ROC AUC: 0.87 (+/- 0.18) [Decision tree]
ROC AUC: 0.85 (+/- 0.13) [KNN]
ROC AUC: 0.98 (+/- 0.05) [Majority voting]
scikit-learn VotingClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_validate
from sklearn.ensemble import VotingClassifier
vc=VotingClassifier(estimators=[('lr', pipe1), ('dt', clf2), ('knn', pipe3)], voting='soft')
scores=cross_validate(estimator=vc, X=X_train, y=y_train, cv=10, scoring='roc_auc')
print("ROC AUC: %0.2f ( +/- %0.2f) [%s]" %(scores['test_score'].mean(), scores['test_score'].std(), 'VotingClassifier'))
ROC AUC: 0.98 ( +/- 0.05) [VotingClassifier]
estimators 매개변수에 분류기 이름과 객체로 구성된 튜플의 리스트를 입력한다.
MajorityVoteClassifier는 vote 매개변수에 상관없이 predict_proba 메서드를 실행할 수 있지만, voting=‘hard’일 경우
predict_proba 메서드는 지원하지 않는다.
VotingClassifier의 fit메서드의 verbose 매개변수를 True로 지정하여 진행과정을 출력할 수 있다.
vc.set_params(verbose=True)
vc.fit(X_train, y_train)
[Voting] ....................... (1 of 3) Processing lr, total= 0.0s
[Voting] ....................... (2 of 3) Processing dt, total= 0.0s
[Voting] ...................... (3 of 3) Processing knn, total= 0.0s
VotingClassifier(estimators=[('lr',
Pipeline(steps=[['sc', StandardScaler()],
['clf',
LogisticRegression(C=0.001,
random_state=1)]])),
('dt',
DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy',
max_depth=1,
random_state=0)),
('knn',
Pipeline(steps=[['sc', StandardScaler()],
['clf',
KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=1)]]))],
verbose=True, voting='soft')
voting=‘soft’ 일 때 predict 메서드는 predict_proba 메서드에서 얻은 가장 큰 확률의 클래스를 예측으로 삼는다.
predict_proba 메서드는 각 분류기의 클래스 확률을 평균하여 반환한다.
vc.predict_proba(X_test[:10])
array([[0.80858947, 0.19141053],
[0.80798659, 0.19201341],
[0.80742142, 0.19257858],
[0.81176637, 0.18823363],
[0.81195778, 0.18804222],
[0.17701319, 0.82298681],
[0.17670572, 0.82329428],
[0.17845724, 0.82154276],
[0.1796252 , 0.8203748 ],
[0.81076201, 0.18923799]])